This is one of those posts that I write mainly for myself in the future, but that maybe can be useful for others developers that want or need to run Visual Basic 6.0 without admin rights on Windows 7 or Windows 10.
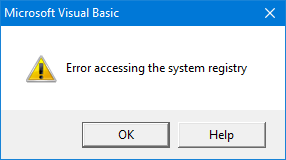
One of the flavors of my MZ-Tools add-in is for Visual Basic 6.0 (yes, there is still quite a few people using it). Visual Basic 6.0 was created and used heavily in a time (Windows 98-Windows XP) when every Windows user was an administrator, so it was not a problem that when building an ActiveX DLL project some registry entries were added to the HKEY_CLASSES_ROOT (HKCR) registry hive, actually to HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE (HKLM) internally. On Windows Vista and higher with the User Account Control (UAC) that changed, so if you run Visual Basic 6.0 without admin rights you get this error when building an ActiveX DLL:
 A solution is of course to run Visual Basic 6.0 with admin rights, and I have been doing it so for some years. But that requires Visual Studio running also with admin rights, to be able to debug an add-in project loaded on Visual Basic 6.0 (if Visual Studio is not running with admin rights, it prompts you to restart with admin rights, but that’s quite annoying). But running Visual Studio all the time with admin rights only because of Visual Basic 6.0, when all the IDEs (Visual Studio, VBA) of my other add-ins wouldn’t require it, is somewhat overkill, and I really wanted to avoid it.
A solution is of course to run Visual Basic 6.0 with admin rights, and I have been doing it so for some years. But that requires Visual Studio running also with admin rights, to be able to debug an add-in project loaded on Visual Basic 6.0 (if Visual Studio is not running with admin rights, it prompts you to restart with admin rights, but that’s quite annoying). But running Visual Studio all the time with admin rights only because of Visual Basic 6.0, when all the IDEs (Visual Studio, VBA) of my other add-ins wouldn’t require it, is somewhat overkill, and I really wanted to avoid it.
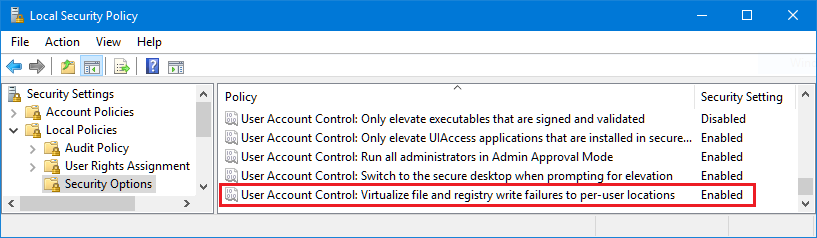
So, I was aware of the Registry virtualization mechanism of UAC, which Microsoft invented precisely for this scenario: an application that required admin rights to write in some keys of the HKLM\Software key of the Registry but that was not allowed to run with admin rights. Since Registry virtualization was not working for Visual Basic 6.0, my first thought was that it no longer existed on Windows 10 (documents say that apps cannot rely on this mechanism forever since it will be removed in some Windows version), or that it needed to be activated at global level. But no, if you open the Local Security Policy and go to Local Policies > Security Options, the setting exists and file and registry write failures are virtualized by default:
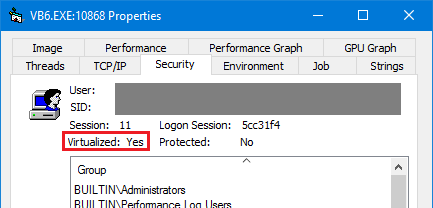
 My second thought was that it needed to be activated per-application. But no, all the documents say the opposite, applications can disable registry or file virtualization by adding a .manifest, which signals to the Windows OS that the application is UAC-compliant (and therefore virtualization is not required). And indeed Process Explorer revealed that vb6.exe runs with virtualization:
My second thought was that it needed to be activated per-application. But no, all the documents say the opposite, applications can disable registry or file virtualization by adding a .manifest, which signals to the Windows OS that the application is UAC-compliant (and therefore virtualization is not required). And indeed Process Explorer revealed that vb6.exe runs with virtualization:
 So, what was happening? Process Monitor to the rescue. I noticed that Visual Basic 6.0 was trying to write to HKCR\TypeLib, getting “access denied”, not directly to HKLM:
So, what was happening? Process Monitor to the rescue. I noticed that Visual Basic 6.0 was trying to write to HKCR\TypeLib, getting “access denied”, not directly to HKLM:
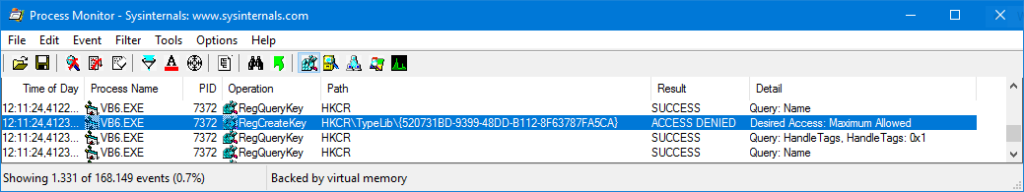 But HKCR is actually a merged view of some keys of HKLM and some keys of HKCU, and clearly the failure was due to the HKLM side.
But HKCR is actually a merged view of some keys of HKLM and some keys of HKCU, and clearly the failure was due to the HKLM side.
Finally, a closer reading of the page Registry Virtualization on MSDN, section Controlling Registry Virtualization, gave me the clue: it happens that not all the keys of HKLM\Software are virtualized by default. In particular, the keys and subkeys of HKLM\Software\Classes, which are used when registering an ActiveX component, are not virtualized by default. Fortunately, you can use the reg.exe tool to query and virtualize them.
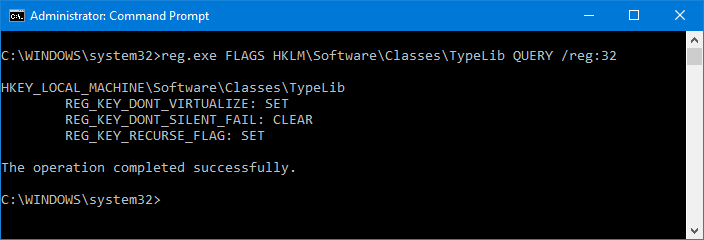
So I launched an elevated (with admin rights) command prompt and queried the HCKR\Classes\TypeLib (actually HKLM\Software\Classes\TypeLib) in 32-bit Registry (Visual Basic 6.0 is a 32-bit executable) with this command:
reg.exe FLAGS HKLM\Software\Classes\TypeLib QUERY /reg:32
Note: the fact that Visual Basic 6.0 is a 32-bit executable and that Process Monitor showed HKCR\TypeLib (that would belong to 64-bit) and not HKCR\WOW6432Node\TypeLib (that would belong to 32-bit) means that both keys (32-bit and 64-bit) are the same.
I got that it is not virtualized (REG_KEY_DONT_VIRTUALIZED: SET):
 To clear that flag I executed the following, that clears the DONT_VIRTUALIZED flag but keeps set the RECURSE_FLAG as before:
To clear that flag I executed the following, that clears the DONT_VIRTUALIZED flag but keeps set the RECURSE_FLAG as before:
reg.exe FLAGS HKLM\Software\Classes\TypeLib SET RECURSE_FLAG /reg:32
Trying to build again the ActiveX DLL causes the same “Error accessing the system registry”, but this time Process Monitor revealed that the problem was in HCKR\WOW6432Node\Interface:
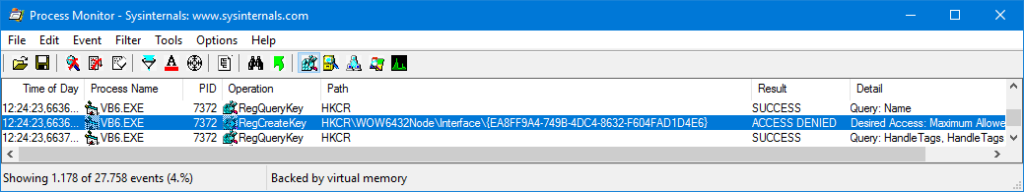 Notice that in this case HCKR\WOW6432Node\Interface is shown, instead of HCKR\Interface, which means that the 32-bit and the 64-bit keys are different.
Notice that in this case HCKR\WOW6432Node\Interface is shown, instead of HCKR\Interface, which means that the 32-bit and the 64-bit keys are different.
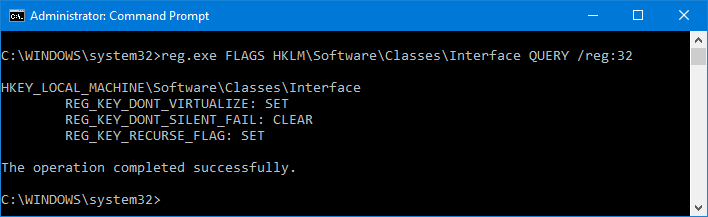
So I queried the flags with this command:
reg.exe FLAGS HKLM\Software\Classes\Interface QUERY /reg:32
And I got that certainly is not virtualized:
 Again, to clear that flag I executed the following, that clears the DONT_VIRTUALIZED flag but keeps set the RECURSE_FLAG as before:
Again, to clear that flag I executed the following, that clears the DONT_VIRTUALIZED flag but keeps set the RECURSE_FLAG as before:
reg.exe FLAGS HKLM\Software\Classes\Interface SET RECURSE_FLAG /reg:32
Trying to build again the ActiveX DLL caused the same “Error accessing the system registry”, but this time Process Monitor revealed that the problem was in HCKR\Interface, so I executed:
reg.exe FLAGS HKLM\Software\Classes\Interface SET RECURSE_FLAG /reg:64
And finally building the ActiveX didn’t cause any error.




 To clear that flag I executed the following, that clears the DONT_VIRTUALIZED flag but keeps set the RECURSE_FLAG as before:
To clear that flag I executed the following, that clears the DONT_VIRTUALIZED flag but keeps set the RECURSE_FLAG as before: